Print (pwd), Change (cd), List (ls), Make (mkdir) Directory
Print Working Directory (pwd)
The pwd command shows your current location in the file system by displaying the absolute pathname of your working directory.
eos$ pwd
The terminal will return the absolute path.
eos$ /mnt/ncsudrive/s/ssrahman
Change Directory (cd)
The cd command changes your current working directory to a specified location.
Command:cd
- Used to change your current location
- Advice: use pwd or ls with or after using cd to ensure you’ve done it right.
eos$ cd pathname
Example
Changing from the E115 Course Locker directory to your home directory. (View animation here)
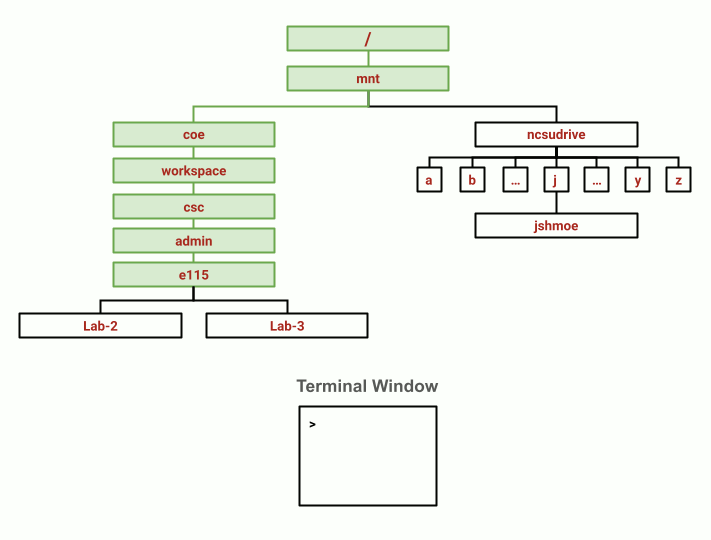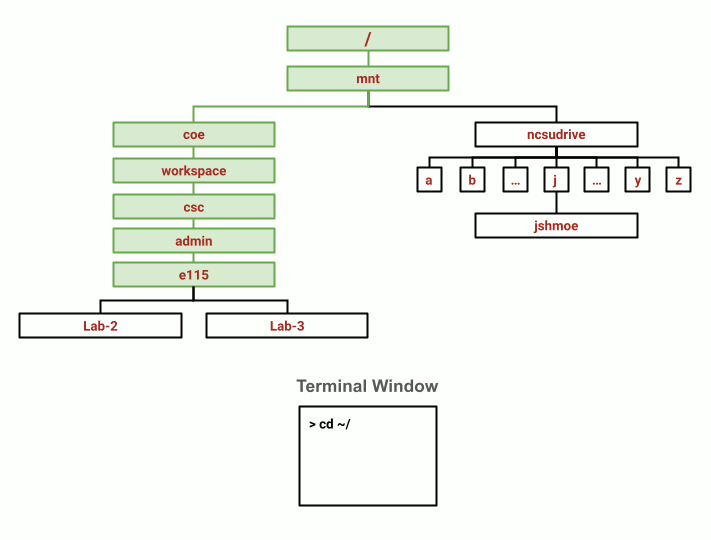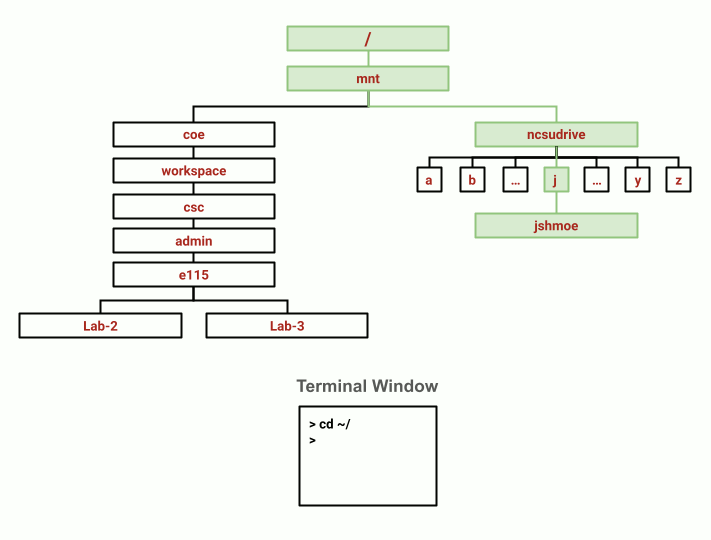
To return to the E115 Course Locker:
eos$ cd /mnt/coe/workspace/csc/admin/e115
List Directory (ls)
List the contents of a directory: ls
The ls command lists the contents of a directory. It’s useful for checking that files are present or confirming a directory’s contents.
- Used to list the contents of a specific directory
- What is the output? the contents of the directory specified, OR of the current directory if nothing is specified
eos$ ls
Or, to list contents of a different directory:
eos$ ls pathname
Common Options:
-l | List contents in long format (includes size, date, owner, permissions, etc.) |
-a | Show all files, including hidden files (those starting with .) |
-al or -la | Combine both options to show all files in long format. Options can be used in any order or used independently of each other. |
Examples
To list the contents of your home directory while you are in it:
eos$ ls
You can also specify another directory by providing a pathname with the ls command.
The contents of the directory will be listed. For example:
MyDocuments MyE115 File.txt
Note: The actual output will vary depending on the directory and the user’s files.
More Examples
I want to list the contents of my HOME directory using a relative path name…
- I am in my home directory, ~/
ls
orls -a
(only if asked for all files)
orls -l(only if asked for info on files)
orls -alorls -la
(only if asked for all files with details)
- I am elsewhere in the file tree
ls ~/
orls -a ~/orls -l ~/orls -al ~/orls -la ~/
Make Directory (mkdir)
Use the make directory (mkdir) command to create a new directory.
Command:mkdir
- Used to create a new directory
- Options:
- -p : creates every directory in the pathname, assuming it doesn’t already exist
- If you are in the location, you can ignore that part of the syntax
- The terminal window is very literal, so make sure you either specify an exact location or be in that location.
Advice: usepwdor ls with or after using cd to ensure you’ve done it right.
eos$ mkdir directory_path
eos$ mkdir -p directory_path
The -p option will create every directory in the pathname, if they don’t already exist.
Examples
I want to create a directory named MyE115 in my home directory…
- I am in ~/:
mkdir MyE115the terminal is CASE SENSITIVE
do an ls after to ensure proper creation - I am elsewhere in the file tree:
mkdir ~/MyE115the terminal is CASE SENSITIVE and there is NO SPACE between the ~/ and the name of the directory
do an ls ~/ after to ensure proper creation
To create a directory called MyE115 in your home directory:
If you are in your home directory:
eos$ mkdir MyE115
If you are not in your home directory:
eos$ mkdir ~/MyE115
Note: ~/MyE115 is the shortcut for the absolute pathname of the directory you wish to create. The complete absolute pathname is /mnt/ncsudrive/j/jshmoe/MyE115
To create a directory called basic_unix inside the MyE115 Directory
eos$ mkdir ~/MyE115/basic_unix
To create a directory called basic_unix inside the MyE115 Directory, if MyE115 does not exist
eos$ mkdir -p ~/MyE115/basic_unix
The -p option creates MyE115 as well as basic_unix
After creating a directory, you can change the directory path to the new directory using cd.
Exercises
- What does the command
lsdo when used with the-loption? - What happens if you use two options at the same time, such as
ls -l -h? - The command
ls -Rlists the contents of directories recursively, which means all subdirectories at each level are listed. The commandls -tlists things by time of last change, with most recently changed files or directories first.- In what order does
ls -R -tdisplay things? Hint:ls -luses a long listing format to view timestamps.
- In what order does
- which of the following commands could
ssrahmanuse to navigate to home directory, which is/mnt/ncsudrive/s/ssrahman?cd .cd /cd /home/ssrahmancd ../..cd ~cd homecd ~/data/..cdcd ..cd ../.
- Moving and copying
If the hypothetical filebooks.datis the only one in your current directory, what is the output of the closinglscommand in the sequence shown below? $ mkdir doc$ mv books.dat doc/$ cp doc/books.dat ../books-saved.dat$ ls
