Github Web Interface
GitHub is a web-based platform for storing code, managing versions, and even hosting websites (via GitHub Pages).
Activate your free Github Account (using your NC State Gmail account) through github.ncsu.edu.
You can create a repository (repo, for short), which is an online collection of files that make up a project1. Each account can have multiple public or private repos. You can track previous versions of a project using version control.
After activating your GitHub account with your NC State email, log in to see your existing repos and recent activity.
To create a new repo, click “New”.
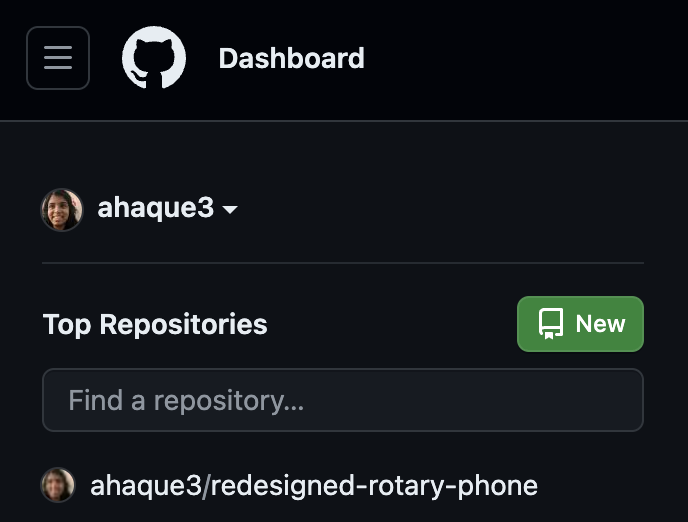
- Name your repository (required) and add a description (optional, but recommended for public repos).
- Choose public or private visibility. Making a repository private means that it is hidden to anyone that you do not explicitly give access to.
- Select “Add a README file” unless you’re importing an existing project.
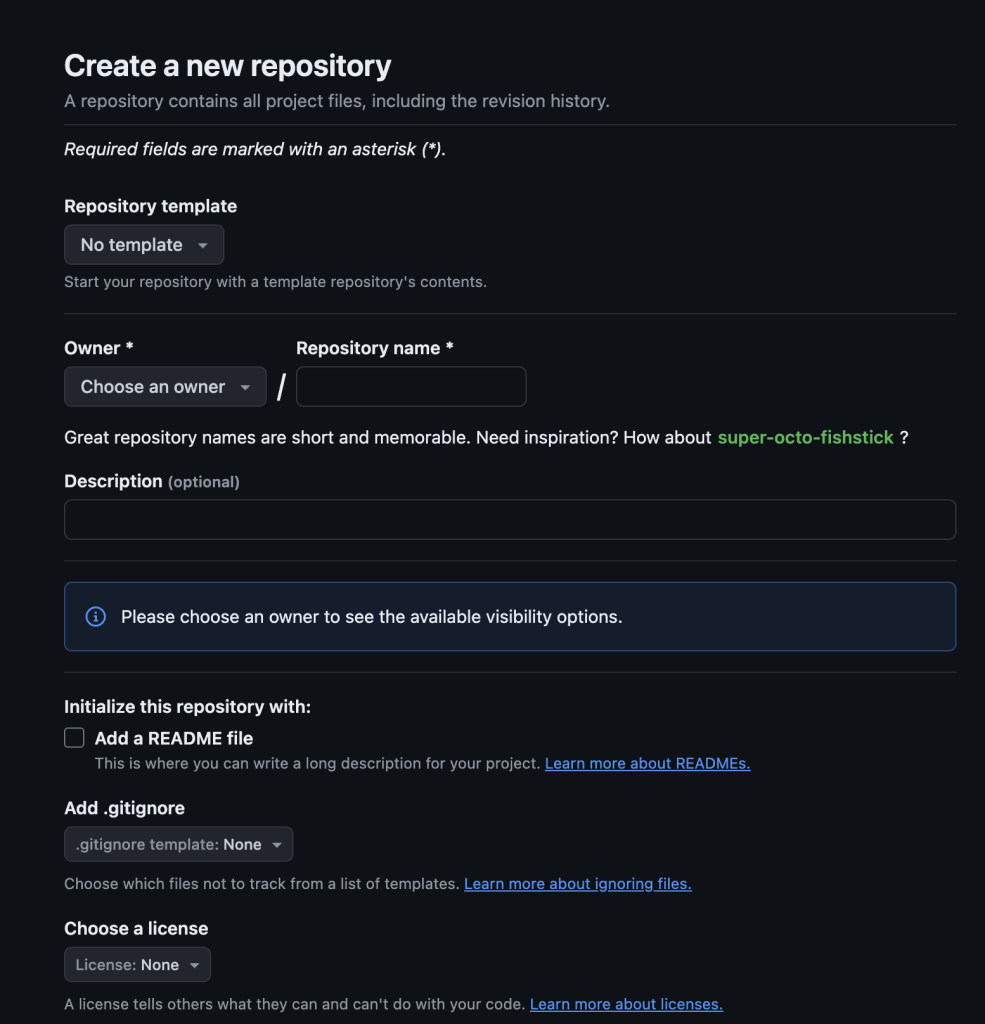
Once you click the “Create Repository” button, you will see the following screen:
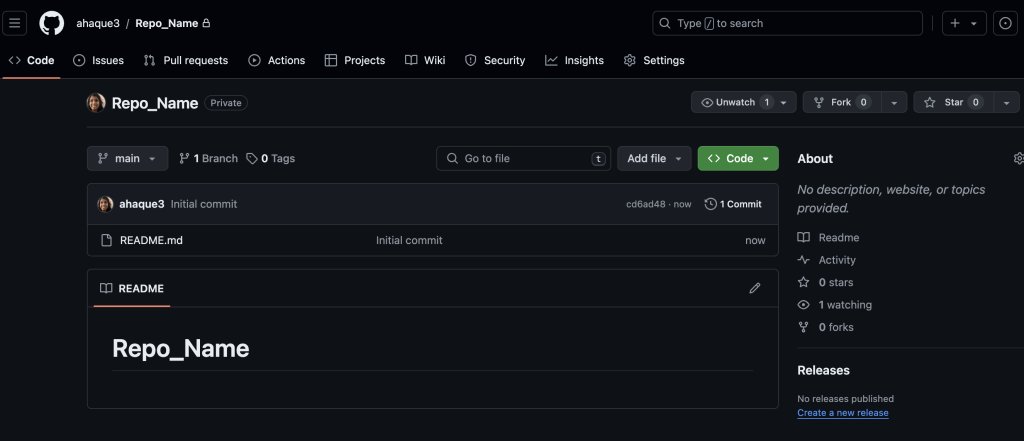
Once created, your repo allows you to:
- Upload files
- Create new files
- Clone or download the repo for local edits
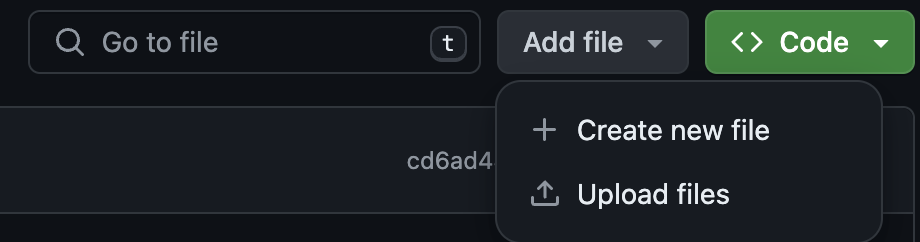
If you choose to “Create new file”, you will see the following screen:
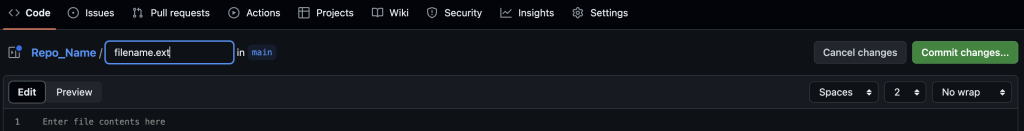
Create your file, name it (with an extension if needed), and then you can commit it by clicking the green “Commit changes” button, which pops up this window:
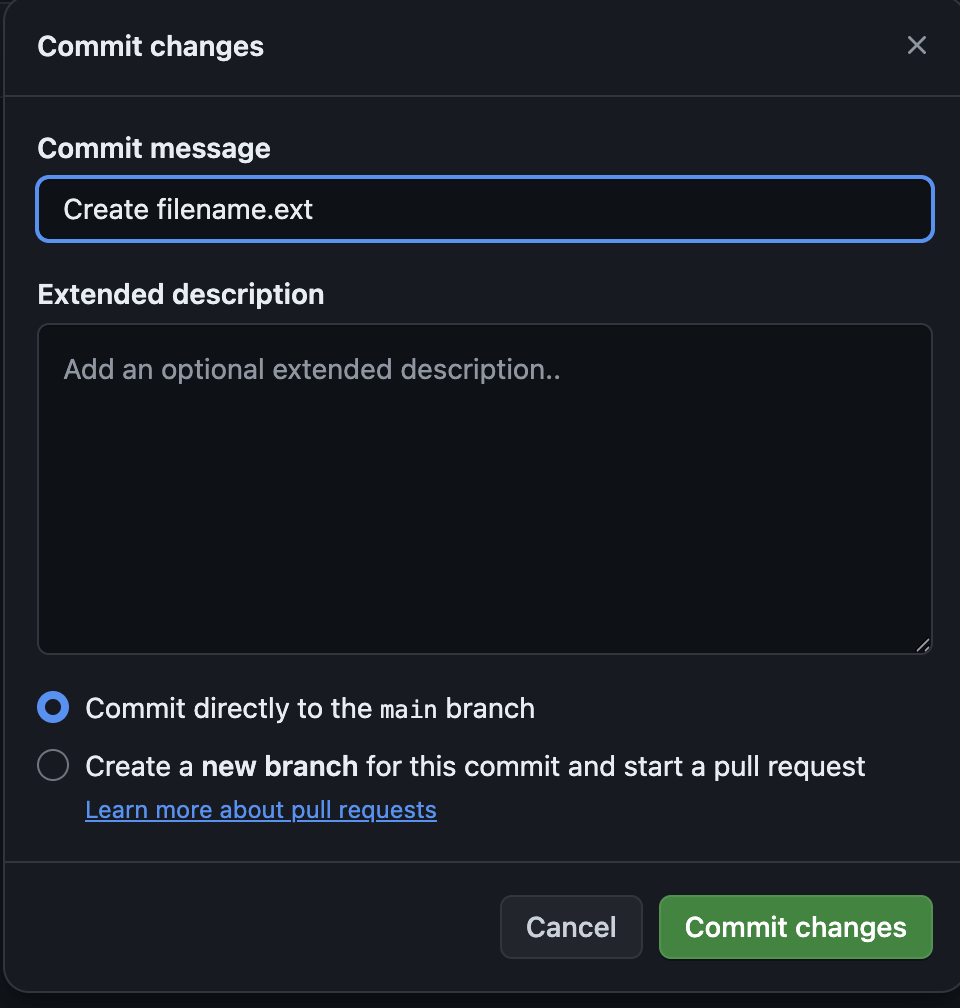
When creating a file:
- Add a commit message describing your changes. This message is a description about what updates were made to the file since the last time it was edited. You can also include an extended description.
- Click “Commit changes” to create/update the file on GitHub! 2
You may keep the file blank to create it, in case you just need the file in the repo.
- Definition of repository: A storage area where a version control system stores the full history of commits of a project and information about who changed what, when. Reference: SW Carpentry. ↩︎
- Definition of commit: To record the current state of a set of files (a changeset) in a version control repository. As a noun, the result of committing, i.e. a recorded changeset in a repository. If a commit contains changes to multiple files, all of the changes are recorded together. Reference: SW carpentry. ↩︎
