Data Operations in UNIX
Working with Files in the NFS
In E 115, you work in an environment that uses the NFS (NCSU File System). You have full access to your own files but only read access to course-provided files, like those in the E115 Course Locker. That means you must copy these files into your personal space before you can modify them. This section introduces three essential commands for managing files: cp (copy), rm (remove), and mv (move or rename).
This page has examples specifically for the NCSU File System, however, cp, rm, and mv are common commands that you can use from any UNIX-based terminal. You can copy, remove, and move files from a file explorer, too, using the GUI…but one of the reasons to learn these commands is that you can use it to automate copying or renaming hundreds of files. Computers are great at aiding in repetitive tasks! However, far too often, we forget that this applies just as much to our use of the computer as it does to the computations we want our programs to perform. We have a vast range of tools available at our fingertips that enable us to be more productive and solve more complex problems when working on any computer-related problem.
We want to teach you how to make the most of the tools you know, show you new tools to add to your toolbox, and hopefully instill in you some excitement for exploring (and perhaps building) more tools on your own.
Sections
Learning Outcomes
Navigate and operate UNIX-based command-line operations.
Chapter Learning Outcomes
- Use Unix commands such as
cp, scp, rm, mv, including with options and arguments. - Use
grepwith options to answer file search questions. - Connect to a remote system using
sshand describe its purpose in secure communication - Use useful shortcuts and keyboard commands to manipulate the terminal more quickly.
- Troubleshoot errors when using Unix commands by interpreting terminal output and correcting syntax
Smartphone Analogy
Voice Commands: Call my Dad’s Cell phone (Smartphone Analogy)
- Go to voice commands
- Find and use the right command
- Ex: Call
- Ex: Text (send a message?)
- Find the right person
- Ex: Dad
- Are there options?
- Ex: which number: cell (not required , used to provide extra information)
- Putting it all together: Call Dad’s Cell
Terminal Commands:
List the contents of ~/ with details
- Connect to terminal
- Find and use the right
command:
- Ex:
ls
- Find the right path
- Ex: ~/
- Are there options? • Ex: want details:
-l
(not required, used to provide
extra information) - Putting it all together:
ls -l ~/
Commands Quick Reference
| Command | Purpose | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
pwd |
Shows the absolute pathname of the user’s current directory | pwd |
ls |
List contents of a directory | |
cd |
Change directory | |
mkdir |
Create a new directory | |
cp |
Copy a file or folder | |
mv |
Move or rename a file | |
rm |
Remove a file or directory | |
clear |
Clear the terminal screen | clear |
man |
View manual page for a command | |
script |
Start a terminal log file | |
Copy (cp)
eos$ cp source_path destination_path
- Copies a file or folder from one location to another
- Also used to rename files and keeps the original
- Advice: Run
lsafter copying to verify. - Use
-rto copy directories
Example: Copy a file named example.txt from my HOME directory to my ~/MyE115 directory…
- I am in
~/cp example.txt MyE115
orcp example.txt MyE115/newName.txt
do an ls after to ensure proper copying
- I am elsewhere in the file tree
cp ~/example.txt ~/MyE115
orcp ~/example.txt ~/MyE115/newName.txt
do an ls after to ensure proper copying
eos$ cp example.txt MyE115/
Example: Copy from the E115 Course Locker
eos$ cp /mnt/coe/workspace/csc/admin/e115/common/lab-3/inlab3.txt ~/
Copy multiple files at once:
eos$ cp source_path1 source_path2 source_path3 destination_path
eos$ cp file1.txt file2.txt ~/destination_folder/
Copy entire directories ( must use -r):
eos$ cp -r directory_path destination_path
eos$ cp -r folder_name/ ~/destination_folder/
Example 1: Copying a Single File in the E115 Course Locker
To copy inlab3.txt to your home directory, while you are in the lab-3 directory:
eos$ cp inlab3.txt ~/

Example 2: Copying a File in the E115 Course Locker, while in your Home Directory
To copy inlab3.txt from the /common/lab-3/ directory of the E115 Course Locker to your home directory, while you are in your home directory, simply append /common/lab-3/ to the end of the absolute pathname for the E115 Course Locker, along with the name of the file you want to copy. Don’t forget the destination pathname! Reminder that the pathname for the E115 Course Locker is: /mnt/coe/workspace/csc/admin/e115
eos$ cp /mnt/coe/workspace/csc/admin/e115/common/lab-3/inlab3.txt ~/
OR
eos$ cp /mnt/coe/workspace/csc/admin/e115/common/lab-3/inlab3.txt ./
Note: since you are located in your home directory, the “./” (dot slash) represents your home directory, and you may use it instead of “~/” while in your home directory.

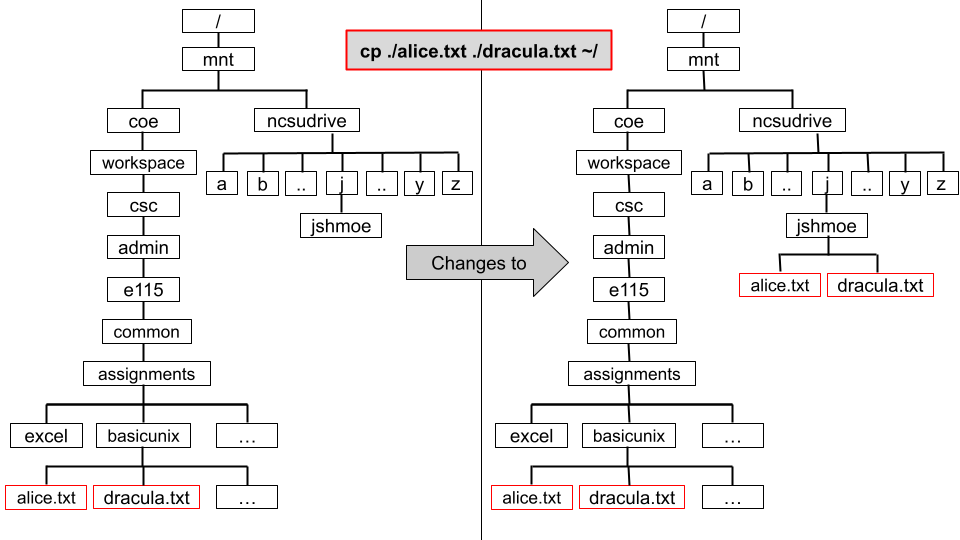
Example 3: Copying Multiple Files
To copy alice.txt and dracula.txt from the basicunix directory to your home directory while you are in the basicunix directory:
eos$ cp ./alice.txt ./dracula.txt ~/
Should I expect an output from the copy command?
No. A successful copy produces no output. If you are receiving output or an error message, you have either typed the directory path incorrectly, or the file does not exist in the specified location.
Removing Files with rm
Use the rm (remove) command to delete files or folders from your NFS space. Deleted files are permanently removed, so be careful when using this command!
Remove files or folders: rm
Command:rm
- Used to delete files or folders from the system
Removing files and folders: an example
I am in ~/ and so is file.txt and folder
Files
rm file.txtorrm -f file.txt
Folders
rm -rf folder
I am elsewhere in the file tree and file.txt and folder are in ~/
Files
rm ~/file.txtorrm -f ~/file.txt
Folders
rm -r ~/folder
Depending on the permissions of the file, rm does not ask for confirmation before deleting. You can force deletion without prompting for confirmation by using -f. Be careful when using –f!
eos$ rm [options] filename
Common Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-r | Remove directories recursively |
-f | Force deletion without confirmation |
-rf | Delete folders and contents without prompts |
-i | Ask before deleting each file |
To delete a folder and all its contents:
eos$ rm -rf old_folder
Will I See Output?
No, unless you use -i. Then you’ll see:
rm: remove regular file 'file.txt'?
Moving or Renaming with mv
Command:mv
eos$ mv source destination
- Used to move a file from one location to another
- Also used to rename files and deletes the original
- Advice: use
lswith or after using cd to ensure you’ve done it right. - Cannot be used within the E 115 course locker. Students lack the permission for it.
Examples
I want to move a file named example.txt from my HOME directory to my ~/MyE115 directory…
- I am in
~/mv example.txt MyE115/newName.txtdo an ls after to ensure proper moving
- I am elsewhere in the file tree
mv ~/example.txt ~/MyE115/newName.txtdo an ls after to ensure proper moving
Example: Rename a File
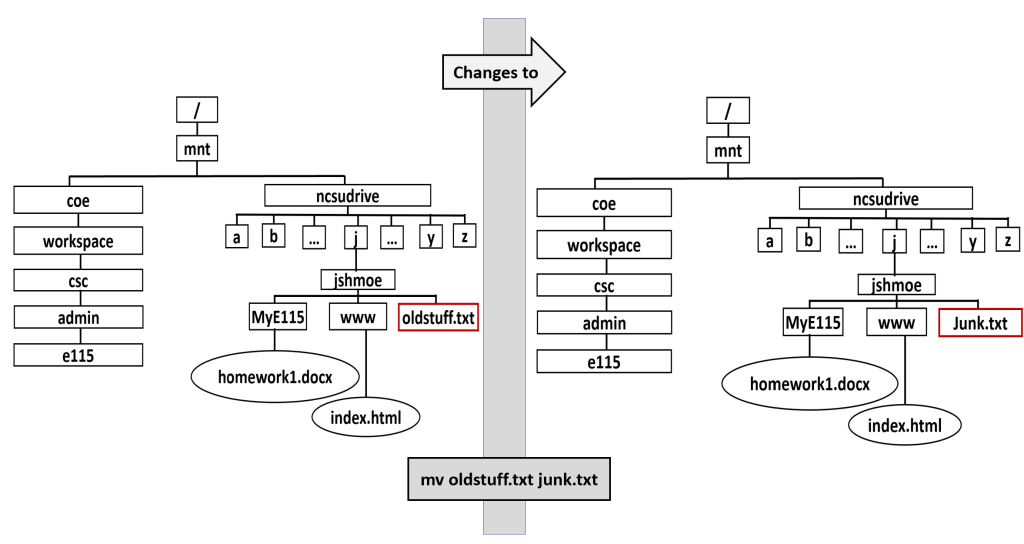
How would you rename the file oldstuff.txt to junk.txt while in your home directory?
eos$ mv oldstuff.txt Junk.txt
Example: Move a File
How would you move the file assignment from your home directory to your MyE115 directory?
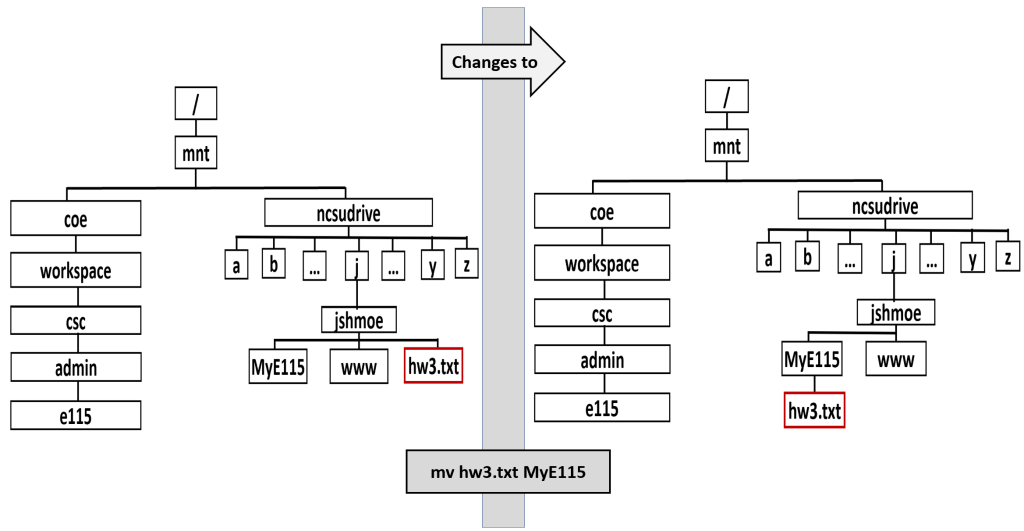
eos$ mv hw3.txt MyE115/
Will I See Output?
No. The mv command is silent unless something goes wrong.
Exercises
Here are a few useful tools:
ping: Test whether a computer is reachable on the network.curl: Download a file or webpage from a URL.find: Search for files by name, type, or modified time.
These aren’t required for this course, but you may use them in your other courses.
