Hardware Summary and Supplemental
Processors
- The processor (CPU) performs the fundamental arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations.
- 64-bit vs 32-bit. The key difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processors is the amount of memory they can address. A 32-bit processor can address up to 4GB (2^32) of RAM, while a 64-bit processor can address up to 18.4 million TB (2^64).
- GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are specialized for rendering graphics and image processing (and machine learning!).
Memory
Read Only Memory (ROM)

Non-volatile: power loss will not affect data
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS): Traditionally stored in ROM. Modern systems use UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which provides more features and a graphical interface.
Random Access Memory (RAM)

Volatile: power loss will lose data
Storage location for data the CPU uses and allows for easy manipulation quickly
Hard Drive
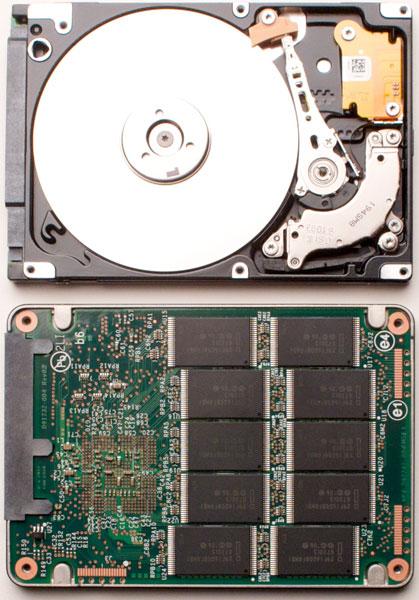

- Stores data.
- Holds applications when not in use.
- Holds files/important documents/music/pictures/etc..
- Makeup:
- Platter, Read/Write Head for traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs).
- Solid State Drive (SSD)
- No moving parts.
- SSD is a solid-state device, so it is truly random access memory (RAM).
- More durable.
- More expensive, although prices have been decreasing.
- No moving parts.
- Interfaces:
- IDE, SCSI, ATA: Older interfaces.
- RAID (configuration): Refers to a configuration for multiple drives for redundancy and performance.
Hard Drive Storage
Tracks: concentric sectors that go around the platter
Disk Sectors: Pie shaped wedges
Tracks and Sectors. Tracks and Sectors denote the location of the information. Modern drives also use advanced formats like 4K sectors.

Removable Storage
- External Hard Drives.
- CD/DVD/Blu-Ray Drives, though optical media are less common for data storage today.
- USB flash drives.
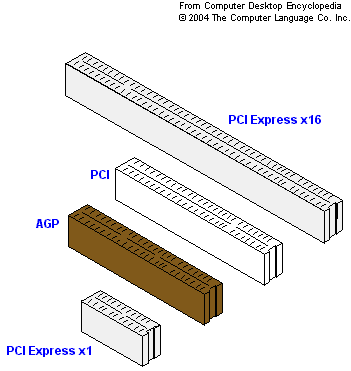
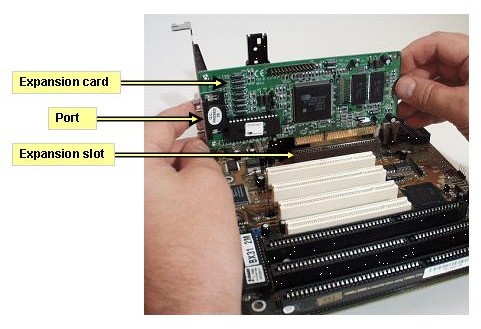
Expansion Slots
- Phased Out:
- AGP (Introduced in 1996) and PCI (Introduced in 1992).
- Current:
- PCI Express (Introduced in 2002), with versions evolving (e.g., PCIe 4.0, PCIe 5.0, and the PCIe 6.0).
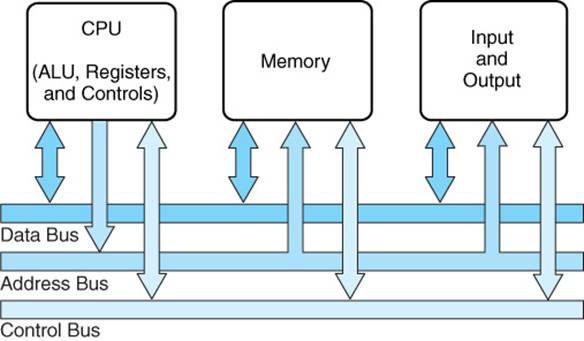
System Bus
Definition of bus: a distinct set of conductors carrying data and control signals within a computer system, to which pieces of equipment may be connected in parallel.
Data Bus: data flows back-and-forth between devices
Address Bus: tells devices where data should go or is coming from
Control Bus: coordinates activity between devices to prevent collisions (corruption of data from simultaneous use of data/address bus)
Updates and Additional Information:
- Processors: Modern CPUs also feature multiple cores, hyper-threading, integrated graphics (in some models), and advanced instruction sets.
- Memory: DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM technology continues to evolve (e.g., DDR4, DDR5).
- Storage:
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs provide significantly faster performance compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
- Interfaces: NVMe and SATA are common for SSDs; IDE and SCSI are largely obsolete for new devices.
- Removable Storage: USB Type-C and Thunderbolt interfaces provide high-speed data transfer for external storage.
- Expansion Slots: PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0 offer greater bandwidth and speed for modern components like GPUs and SSDs.