Networking Summary and Supplemental

Networking Hardware
Hub:
Connects computers and other hardware
Switch: Like a hub, but with an intelligent design
Firewall:
- Can be either hardware or software
- Prevents unauthorized communication via a set of predetermined rules
Router
Exists between networks
Commonly a LAN and the Internet
Uses a routing configuration table
Different types for different environments

Internet Connection Sharing
- Home broadband Routers
- Office Network Routers
- Major Traffic Routers
Wired Media
Ethernet Cable
- 2 pairs of cables
- CAT5 and CAT6 wire, RJ-45 connector
- 100 m (320 ft) without signal loss
Coaxial Cable
- Copper wire; Durable and insulated
- 500 m without signal loss
- Single direction data transfer
Fiber Optics
- Uses pulses of light
- Travels at the speed of light
- 145 km without signal loss
- Primarily choice for telecommunication industry
- Example: Verizon Fios, Google Fiber, ATT Fiber
Wireless Media
- Wi-Fi
- Standardized by the IEEE
- 802.11 groups: a, b, g, n
- MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)
- Bluetooth
- Cell phones


Network Topology
Area networks
LAN – WAN – MAN and VLAN
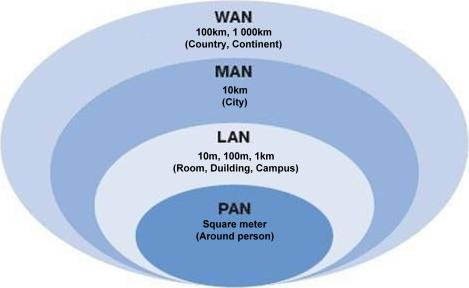
VLAN is virtual LAN (setting up a LAN, but with software). Think of a ‘virtual switch’.
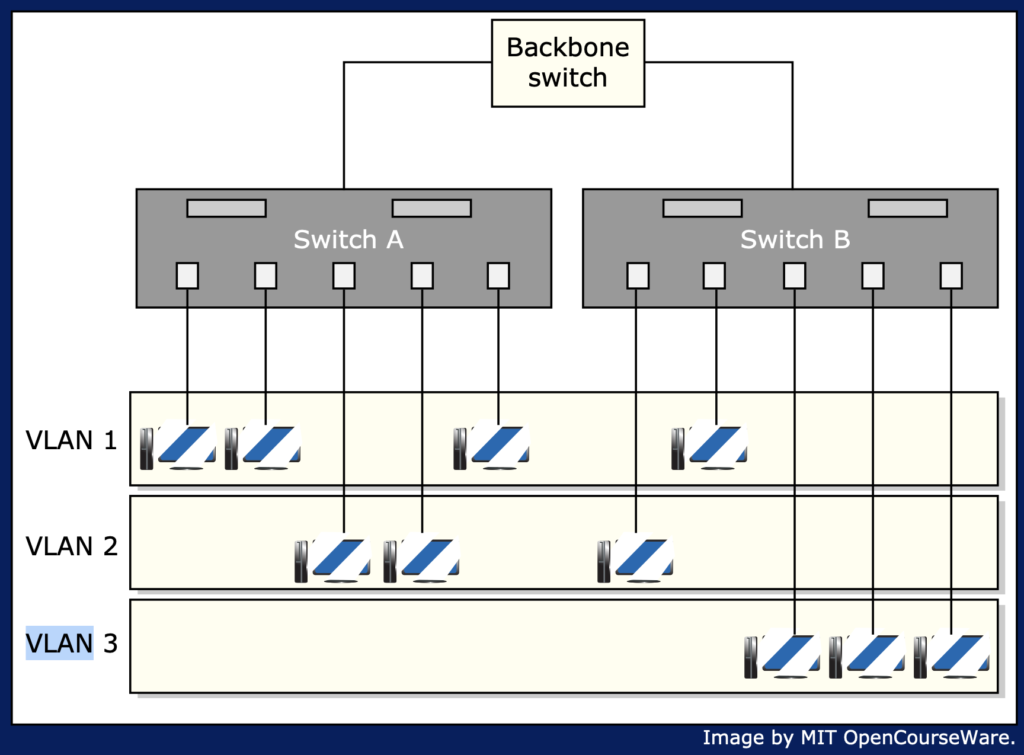
Configurations
| Description | Advantage | Disadvantage | |
| Tree: | collections of star networks arranged in a hierarchy | Reduces wiring | A failed node will fragment the network |
| Star: | computers are connected by one central device known as a concentrator | High wire usage | Concentrator failure disables the network |
| Bus: | set of clients is connected using a single shared connection line known as a bus. The single connection line uses CSMA | Cheapest and easiest | Line break drops network |
| Ring: | Nodes are connected in a circular configuration. Data travels in one direction | Line breaks doesn’t completely disable computers | Isolation issues can occur if a device fails |
Layers
| Layer | Example |
| Link Layer | Ethernet |
| Internet Layer | Internet Protocol (IP) |
| Transport Layer | Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) |
| Application Layer | HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) |
Domain Name Server
- Why domain names?
- user friendly
- no need to remember IP address
- load balancing
- same name maps to changing IP address
- decoupling
- can move server to different network, ISP, etc.
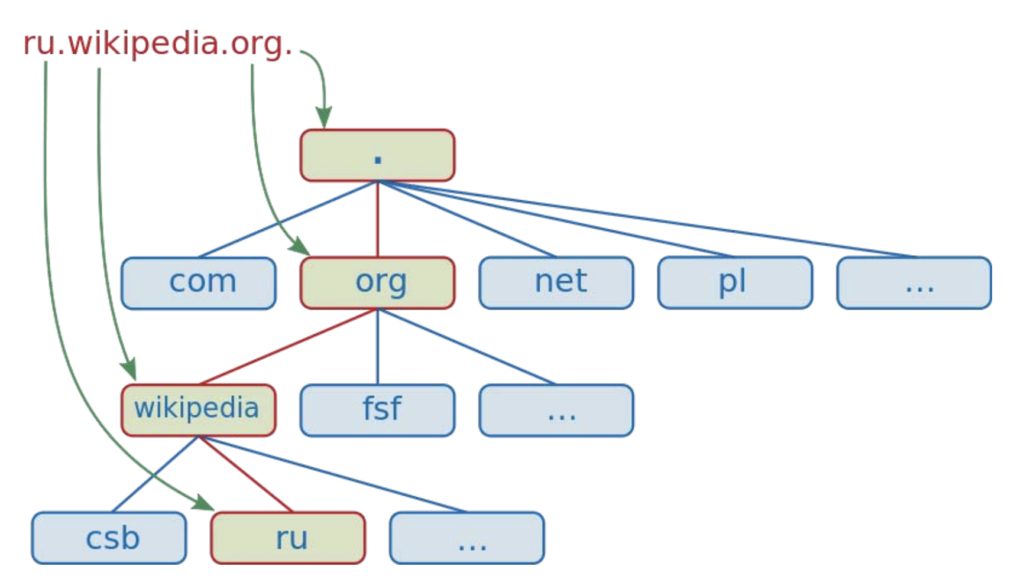
Domain names are hierarchical!
SSH
- Program that enables a computer to log into another computer over a network
- Works securely due to tunneling and encryption
- Secure against:
- Spoofing
- Source Routing
- No protection from root access